Is there a silver bullet to address Scope 3 emissions challenges?
In an era of increased environmental awareness, the concept of Scope 3 emissions has gained significant traction. These emissions, though indirect, play a crucial role in a company’s environmental footprint. In this blog, we will understand Scope 3 emissions, explore why they demand attention, and discuss strategies for effectively addressing them. Let’s delve into the world of sustainable procurement .
Understanding Scope 3 Emissions
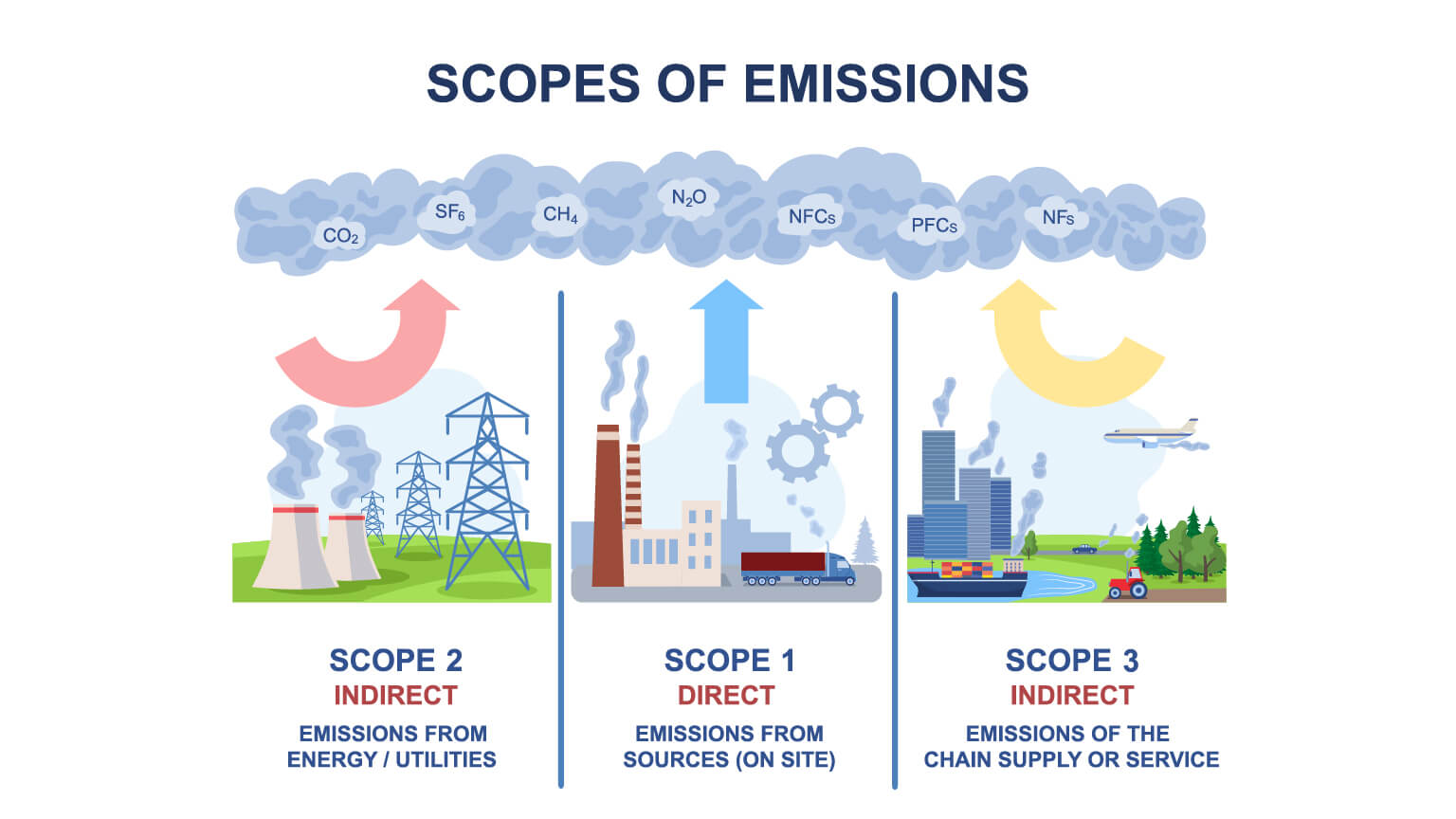
Scope 3 emissions represent the indirect greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that occur outside an organization’s direct control but are associated with its activities. Unlike Scope 1 emissions (direct emissions from owned or controlled sources) and Scope 2 emissions (indirect emissions from purchased energy), Scope 3 emissions cover a broader spectrum. They include emissions generated throughout the supply chain, encompassing activities such as purchased goods and services, transportation and distribution, waste disposal, and business travel.
Why Scope 3 Emissions Matter?
Comprehensive Carbon Footprint: Scope 3 emissions provide a holistic view of a company’s environmental impact. They account for the majority of emissions in many industries, often exceeding Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions combined. Addressing Scope 3 emissions is essential for organizations aiming to understand and reduce their overall carbon footprint effectively.
Supply Chain Resilience: Businesses cannot achieve sustainability goals in isolation. Suppliers and partners have a significant influence on environmental performance. By addressing Scope 3 emissions, organizations can foster collaboration with suppliers, promote sustainable practices, and build a resilient supply chain that aligns with their sustainability objectives.
Reputation and Stakeholder Expectations: In an era of increased transparency and consumer activism, companies are under growing pressure to demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility. Addressing Scope 3 emissions showcases a proactive approach to sustainability, enhancing brand reputation and meeting stakeholder expectations.
Are we doing enough?
There are enough examples to demonstrate that companies are taking proactive sustainable steps to control scope 3 emissions. Unilever and IKEA are prime examples of companies that have prioritized controlling Scope 3 emissions in their supply chains. Unilever has made sustainability a core focus, actively engaging with suppliers to reduce emissions and sourcing 100% of its agricultural raw materials sustainably. Through initiatives like the Sustainable Living Plan, Unilever aims to decouple growth from environmental impact while improving livelihoods. On the other hand, IKEA takes a comprehensive approach, focusing on sustainable sourcing, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. With ambitious goals of becoming climate positive by 2030, IKEA is committed to reducing its emissions and inspiring positive change throughout the industry. There are others like,Apple, Schneider Electric, Walmart etc. Who have taken proactive steps to address scope 3 challenges. Addressing Scope 3 emissions is crucial for organizations committed to sustainability and environmental stewardship. By understanding the scope of emissions beyond direct control, businesses can make informed decisions and implement strategies that drive significant positive change.
Digitising procurement – Your silver bullet
Digitizing procurement processes offers numerous opportunities to reduce Scope 3 emissions. It enhances supplier management, improves transparency, provides data-driven insights, facilitates collaboration, enables paperless processes, and supports lifecycle analysis. By leveraging digital technologies, organizations can drive sustainable procurement practices and contribute to meaningful emissions reductions throughout their supply chains. Zoglix – A Moglix company has been working with organization to help the digitize their procurement supply chain at rapid yet sustainable pace. Know how know how
How can Digitising procurement help?
Efficient Supplier Management: Digitization allows for streamlined supplier management processes, including onboarding, communication, and performance tracking. By centralizing supplier data and interactions, organizations can easily assess suppliers’ sustainability practices and evaluate their emissions performance. This information enables informed decision-making when selecting suppliers with lower environmental impacts, thus reducing Scope 3 emissions.
Enhanced Transparency: Digital procurement platforms can provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, enabling organizations to track and monitor key sustainability metrics. This transparency allows for better identification of emission hotspots, optimization of transportation routes, and identification of opportunities for improvement throughout the supply chain. It also facilitates collaboration with suppliers to share data and work together towards emission reduction goals.
Data-Driven Insights: Digitized procurement systems generate vast amounts of data, which can be leveraged to gain insights and identify opportunities for emissions reduction. Analyzing this data helps identify inefficiencies, optimize procurement processes, and make informed decisions that contribute to lower Scope 3 emissions. For example, data analysis can highlight areas where waste can be reduced, energy consumption can be optimized, or transportation routes can be consolidated.
Collaboration and Communication: Digital platforms enable seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers, allowing organizations to share sustainability goals, provide guidance, and collaborate on emission reduction initiatives. Real-time communication and data sharing foster a sense of shared responsibility and enable suppliers to align their practices with sustainability objectives, ultimately reducing Scope 3 emissions.
Paperless Processes: Digitization reduces the need for paper-based documentation, such as purchase orders, invoices, and contracts. By shifting to electronic documentation and automated processes, organizations can significantly reduce paper consumption and associated emissions from paper production, transportation, and waste disposal.
Lifecycle Analysis: Digital procurement systems can integrate with lifecycle analysis tools to assess the environmental impact of products or services throughout their lifecycle. This analysis helps identify opportunities for reducing emissions at each stage, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. By considering environmental factors during procurement decision-making, organizations can choose suppliers and products with lower lifecycle emissions, thereby reducing Scope 3 emissions.
It’s time for businesses to acknowledge their role in shaping the environmental impact of their supply chains and take proactive steps to address Scope 3 emissions. By doing so, they not only contribute to a more sustainable planet but also gain a competitive advantage